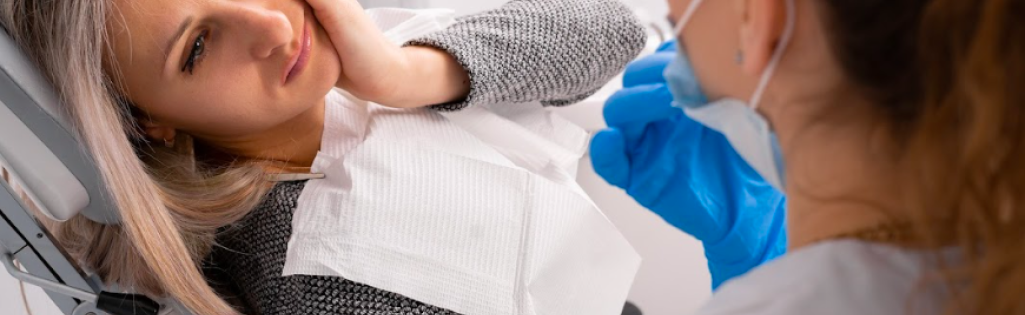
According to the World Health Organization, nearly 3.5 billion people have been affected by oral problems. However, this doesn’t mean all these problems require immediate attention. In contrast to these, there are dental emergencies, which could affect anyone anywhere. (1)
This could mean dental injuries—dental abscess, severe toothache, severe soft tissue injury, cracked and knocked-out tooth, or partially dislodged tooth—that require urgent action. If left untreated, they may get way worse and affect your overall oral health.
So, when you are faced with a dental emergency, what steps should you take?
1. Contact your dentist
No matter what type of dental emergency you’re facing, one of the most important steps is to contact your dentist as soon as possible. Explain your situation clearly; they’ll let you know if you need to rush in or if it can wait for a regular appointment. Quick action can make a big difference.
Here’s a tip: keep your dentist’s emergency contact information readily available. Consider saving it on your phone or posting it somewhere visible in your home. This can save valuable time in an emergency situation.
But if you don’t have one yet, look for trusted dental health providers, like Clear Smiles Dental or others near you, so you know exactly who to call in a dental emergency.
2. Rinse your mouth
Once you’ve contacted a dentist, they would ask you to visit their clinic and attend to the emergency. But you could take other helpful steps, in case they won’t be available, or it will take some time before they tend to you.
For instance, you can rinse your mouth gently with warm water; this simple action can help you out in more than one way. First, it will wash away the dirt and blood blocking the view so that you know what is happening. The warm water can also calm down the area and provide temporary relief. However, remember to use warm water, not hot water, to avoid causing further discomfort.
3. Control bleeding
If your dental emergency involves bleeding, it has to be stopped. You can apply a clean piece of cloth or gauze to the area of bleeding and press it firmly for about 15 to 20 minutes. If the bleeding persists, chances are there could be a deeper problem. This is when you have to move quickly and visit the emergency room.
4. Go to the ER if necessary
While most dental emergencies can be handled by a dentist, there are a few situations where you should go to the emergency room. These include:
- Severe trauma to your face or jaw
- Uncontrolled bleeding
- Difficulty breathing or swallowing
- Signs of a severe infection, like high fever or facial swelling
Emergency rooms are equipped to handle these more serious situations; they can provide immediate care and, if necessary, refer you to a dental specialist.
5. Manage pain
Dental emergencies can be really painful, but there are things you can do at home. Over-the-counter painkillers like ibuprofen or Tylenol can help with pain and swelling. Just be careful not to put aspirin or any other painkiller directly on your gums. It can burn your gums and make things worse. (2)
6. Treat infections
Some dental emergencies, like abscesses, can be serious if left untreated. Signs of an abscess include severe, persistent toothache, fever, swelling in your face or cheek, a bump on your gum that looks like a pimple, and a bad taste in your mouth. If you notice these symptoms, it’s crucial to seek dental care immediately.
In the meantime, you can gently cleanse your mouth with a mild salt water solution. Mix half a teaspoon of table salt in a cup of warm water and swish it around your mouth for about 30 seconds before spitting it out. This can help draw out some of the infection and provide temporary relief.
Things to do for specific types of dental emergencies
There are different kinds of dental emergencies, and each situation may require a different approach. Here are things you can do:
For knocked-out teeth
Each year, more than 5 million people in the U.S. suffer from knocked-out teeth. The same things can happen to you. If so, don’t panic—it might be possible to save it. (3)
First, find the tooth. Hold it by the top part, not the root. Rinse it off gently, but don’t scrub it or remove any stuff stuck to it. If you can, put the tooth back in the hole where it came from. Gently push it in and hold it there. If you can’t do that, keep the tooth wet; you can put it in a small container of milk or hold it in your mouth next to your cheek.
The goal is to get to a dentist as fast as possible—within an hour if you can—for the best chance of saving your tooth.
For loose fillings or crowns
Losing a filling or crown could be painful and leave your tooth open to trouble. If you can find the missing piece, you can try using dental cement from the drugstore to temporarily fix it. It’s not a permanent fix, but it can protect your tooth until you can see a dentist.
If you don’t have dental cement, a little toothpaste or denture adhesive may do in a pinch. But remember, it’s only a temporary solution. You’ll need to get it fixed by a dentist as soon as possible.
For broken teeth
A broken or chipped tooth can be painful; it can leave sharp edges that might cut your tongue or cheek. During this time, rinse your mouth with warm water to clean the area. You can also ice the area outside your cheek near the broken tooth to help reduce swelling and temporarily relieve pain.
If you can, save any pieces of the tooth that have broken off; your dentist might be able to reattach them. Meanwhile, cover any sharp edges with dental wax (available at drugstores) or even a bit of sugar-free chewing gum to protect your mouth until you can see a dentist.
Wrapping up
Dental emergencies can be nerve-racking for sure, but knowing these steps may help you approach the situation calmly and effectively. The bottom line is to act quickly, stay calm, and seek professional assistance as soon as possible. With these steps, you can reduce pain and enhance the possibilities of a positive outcome.
References
- “Oral health”, Source: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/oral-health#:~:text=Oral%20diseases%2C%20while%20largely%20preventable,affect%20nearly%203.5%20billion%20people.
- “Toothache: First aid”, Source: https://www.mayoclinic.org/first-aid/first-aid-toothache/basics/art-20056628#:~:text=Consider%20taking%20a%20pain%20reliever,may%20burn%20your%20gum%20tissue.
- “Avulsed Tooth”, Source: https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/21579-avulsed-tooth#:~:text=Every%20year%2C%20more%20than%205%20million%20people%20in%20the%20U.S.%20have%20their%20teeth%20knocked%20out%20(avulsed).
An AVM or arteriovenous malformation forms when arteries connect directly to veins. This direct connection forms a high-pressure shunt or fistula. The veins are not able to handle the pressure of the blood coming directly from the arteries. The veins stretch and enlarge to create a “nidus”. Usually there are multiple feeding vessels in an AVM and many draining veins.
Full medical glossaryAn abbreviation for luteinising hormone, which is a hormone produced by the pituitary gland.
Full medical glossary