Intermittent fasting (IF) is often suggested as a health boost and method to reverse the symptoms of diabetes, however, the outcome appears to be age-dependent. The latest research from the Munich Hospitals team including Prof. Dr Stephen Herzig (feature pic) and Prof. Dr Alexander Bartelt (pictured below), shows that chronic intermittent fasting disrupted the development of insulin-producing beta cells in young mice. These findings naturally raise concerns about potential risks for humans, especially teenagers.
Key research outcomes include:
- Intermittent fasting during teenage growth affects the development of beta cells
- Beta cells fail to mature properly
- Effects on insulin production
 What are the potential harms and benefits of intermittent fasting?
What are the potential harms and benefits of intermittent fasting?
“Intermittent fasting is known to have benefits, including boosting metabolism and helping with weight loss and heart disease. But until now, its potential side effects weren’t well understood,” says Alexander Bartelt, the Else Kröner Fresenius Professor and Chair of Translational Nutritional Medicine at Technical University of Munich (TUM). In a recently published study, the team shows that intermittent fasting during adolescence could have long-term negative effects on metabolism.
Fasting improves metabolism in older mice, but not in the young
The researchers studied three groups of mice: adolescent, adult, and older animals. The mice remained without food for one day and were fed normally on two days. After ten weeks, insulin sensitivity improved in both the adult and older mice, meaning that their metabolism responded better to insulin produced by the pancreas. This is key to regulating blood sugar levels and preventing conditions like type 2 diabetes.
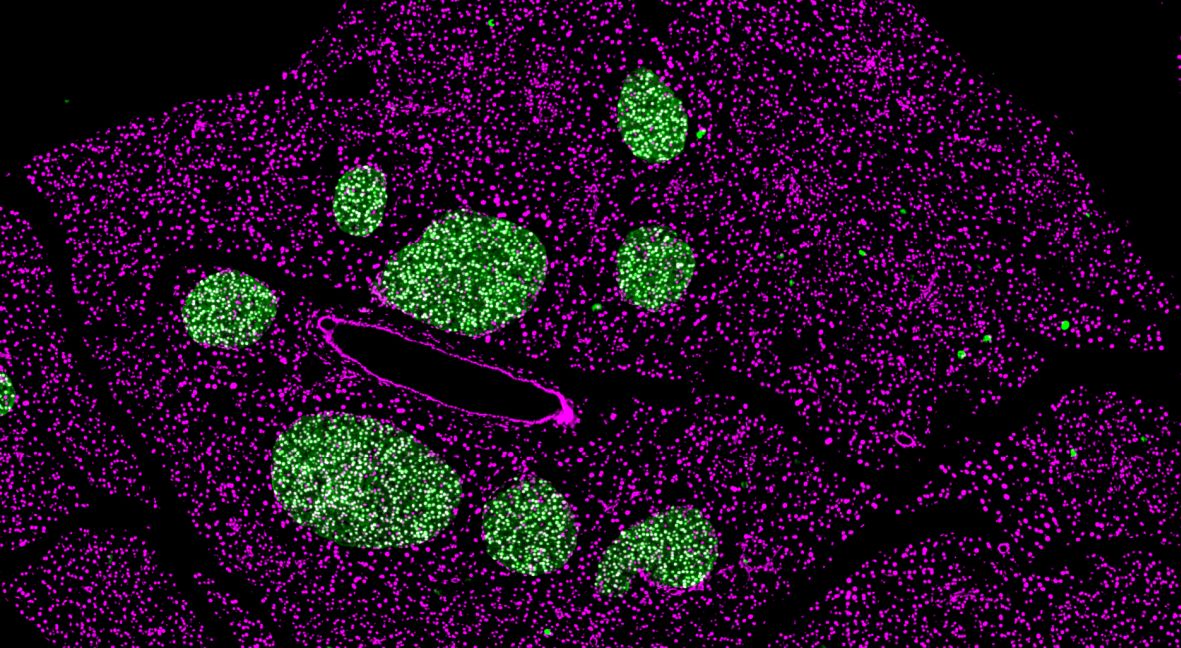 Decline in beta cell function
Decline in beta cell function
However, the adolescent mice showed a troubling decline in their beta cell function, the insulin-producing cells of the pancreas. Insufficient insulin production is linked to diabetes and disrupted metabolism. “Intermittent fasting is usually thought to benefit beta cells, so we were surprised to find that young mice produced less insulin after the extended fasting,” explains Leonardo Matta from Helmholtz Munich, one of the study’s lead authors.
Picture caption: The researchers investigated the impact of intermittent fasting on the beta cells. In the pancreas of mature mice, no negative effects on the beta cells were observed (here stained green).
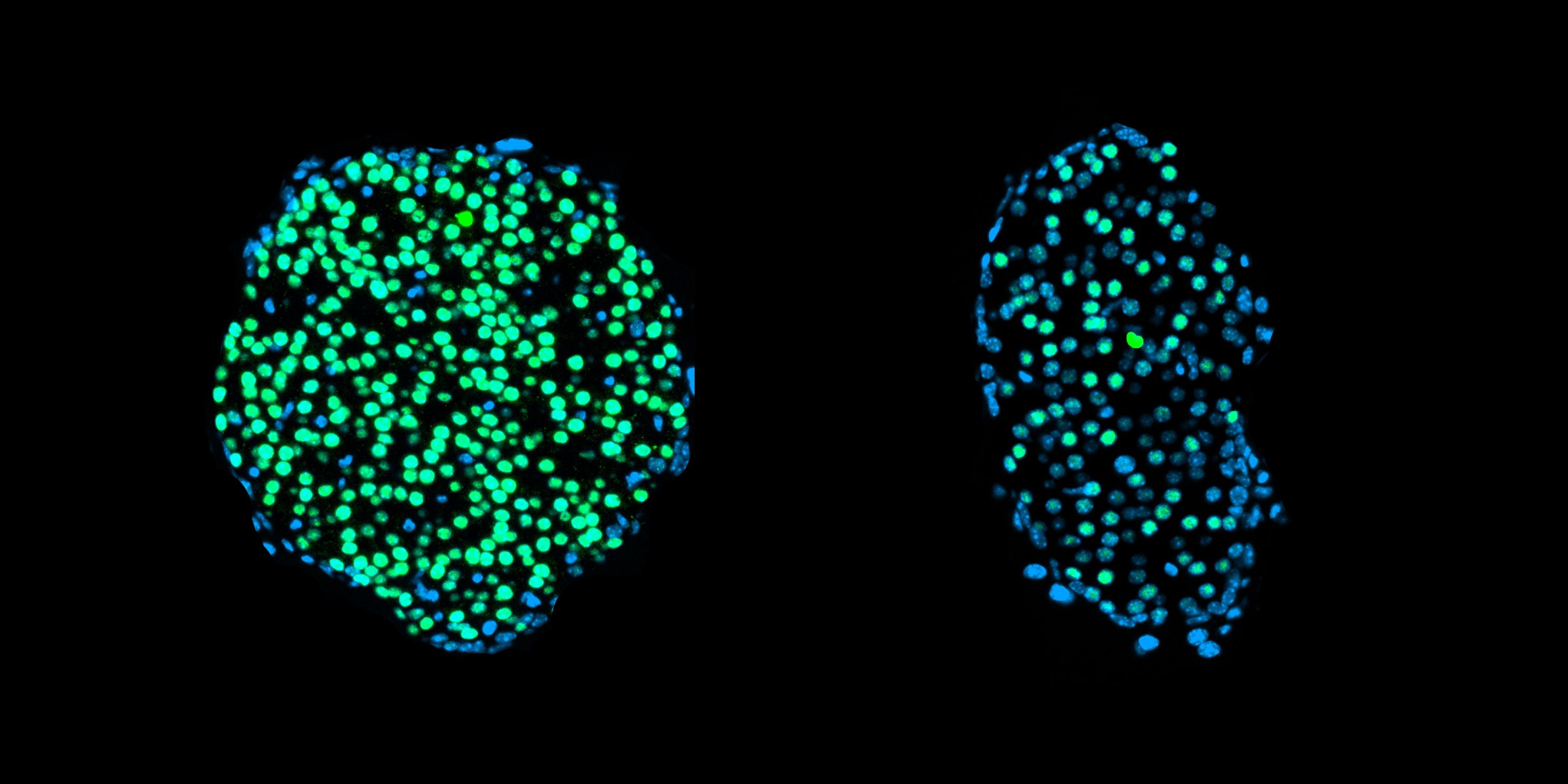 Defective beta cells resemble those of type 1 diabetes patients
Defective beta cells resemble those of type 1 diabetes patients
The researchers used the latest single-cell sequencing to uncover the cause of the beta cell impairment. By examining the blueprint of the pancreas, the team found that the beta cells in the younger mice failed to mature properly. “At some point, the cells in the adolescent mice stopped developing and produced less insulin,” says Peter Weber from Helmholtz Munich, also a lead author. Older mice, whose beta cells were already mature before the fasting began, remained unaffected.
Picture caption: The image shows Langerhans islets after chronic intermittent fasting. On the left are those of an adult animal, and on the right are those of a young animal. The beta cells of the pancreatic Langerhans islets produce insulin. The Langerhans islets of the young animal exhibit fewer fully matured beta cells, which are stained green in this image.
Findings from the mouse study could also be relevant to humans
The team compared their mouse findings to data from human tissues. They found that patients with type 1 diabetes, where beta cells are destroyed by an autoimmune response, showed similar signs of impaired cell maturation. This suggests that the findings from the mouse study could also be relevant to humans.
“Our study confirms that intermittent fasting is beneficial for adults, but it might come with risks for children and teenagers,” says Stephan Herzig, a professor at TUM and director of the Institute for Diabetes and Cancer at Helmholtz Munich. “The next step is digging deeper into the molecular mechanisms underlying these observations. If we better understand how to promote healthy beta cell development, it will open new avenues for treating diabetes by restoring insulin production.”
Publication:
Matta, L., Weber, P., Erener, S. et al., Chronic intermittent fasting impairs β cell maturation and function in adolescent mice, Cell Reports (2025). DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2024.115225.









